PPR, or polypropylene random copolymer, is a type of plastic commonly used in plumbing systems for the transportation of potable water. PPR pipes are available in three different types, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will explore the three types of PPR in detail.
PPR Type 1
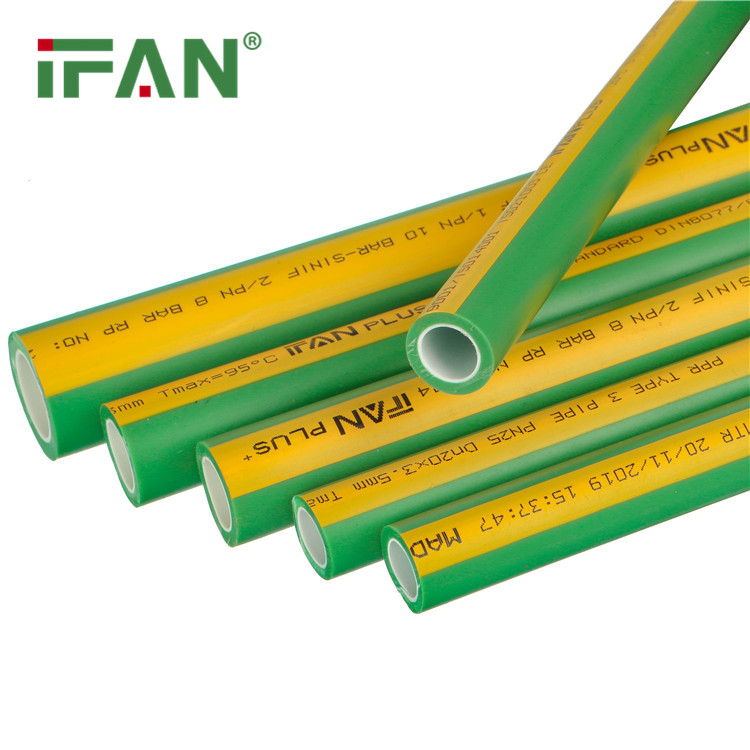

PPR Type 1 pipes are the most commonly used type of PPR pipes. They are suitable for both hot and cold water supply systems in residential and commercial buildings. Here are some key features of PPR Type 1 pipes:
- Pressure Rating
PPR Type 1 pipes have a pressure rating of PN10, which means they can handle a maximum pressure of 10 bars or 145 psi. This pressure rating is suitable for applications with moderate pressure requirements, such as household plumbing systems.
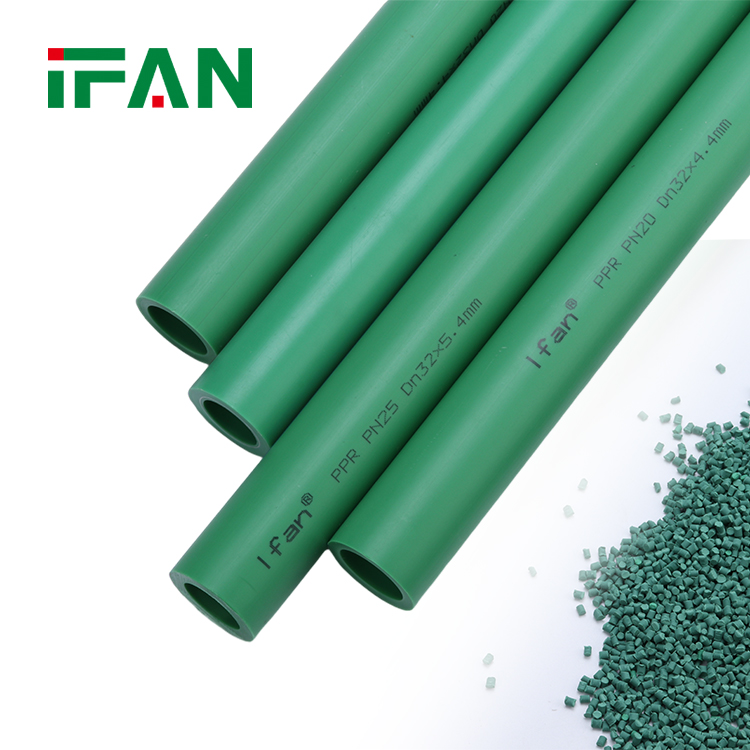

- Applications
PPR Type 1 pipes are commonly used in various applications, including:
- Potable water supply systems in residential buildings.
- Water supply systems in commercial buildings, such as hotels, offices, and schools.
- Plumbing systems in hospitals, laboratories, and other healthcare facilities.
- Irrigation systems in residential gardens and small agricultural fields.
- Advantages
The advantages of PPR Type 1 pipes include:
- Excellent chemical resistance, ensuring the purity and safety of the transported water.
- High-temperature resistance, allowing them to withstand hot water without deformation.
- Low thermal conductivity, reducing heat loss from the water inside the pipes.
- Long service life, as PPR Type 1 pipes are resistant to corrosion and scaling.
PPR Type 2
PPR Type 2 pipes are designed for applications requiring higher pressure ratings than PPR Type 1 pipes can handle. Here are the key features of PPR Type 2 pipes:
- Pressure Rating
PPR Type 2 pipes have a pressure rating of PN16, enabling them to handle a maximum pressure of 16 bars or 232 psi. This higher pressure rating makes PPR Type 2 pipes suitable for applications with higher water pressure requirements.
- Applications
PPR Type 2 pipes are commonly used in the following applications:
- Water supply systems in larger residential buildings, such as apartment complexes.
- Water supply systems in commercial and industrial buildings with higher water pressure demands.
- Irrigation systems in medium-sized agricultural fields.
- Industrial applications requiring higher pressure water transport, such as manufacturing plants.
- Advantages
The advantages of PPR Type 2 pipes include:
- Excellent chemical resistance, ensuring the safe transport of various fluids.
- High-temperature resistance, making them suitable for hot water supply systems.
- Good impact strength, reducing the risk of damage during installation or use.
- Easy installation, as PPR Type 2 pipes can be joined using heat fusion methods.
PPR Type 3
PPR Type 3 pipes are specifically designed for extreme high-pressure applications. Here are the key features of PPR Type 3 pipes:
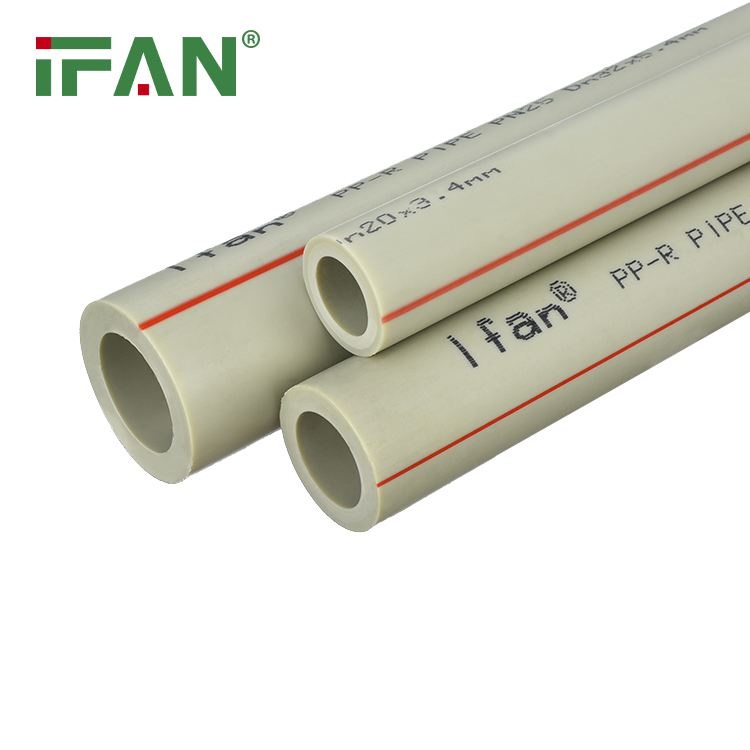

- Pressure Rating
PPR Type 3 pipes have a pressure rating of PN20, allowing them to handle a maximum pressure of 20 bars or 290 psi. This high-pressure rating makes PPR Type 3 pipes suitable for applications with very high water pressure requirements.
- Applications
PPR Type 3 pipes are commonly used in the following applications:
- Industrial applications requiring the transport of aggressive chemicals or fluids under high pressure.
- Chemical processing plants, where the resistance to chemicals and high pressures is crucial.
- Oil refineries, where PPR Type 3 pipes are used for various processes.
- Power generation facilities, where high-pressure water systems are essential.
- Advantages
The advantages of PPR Type 3 pipes include:
- Excellent chemical resistance, ensuring the safe transport of aggressive chemicals.
- High-temperature resistance, making them suitable for extreme temperature applications.
- High-pressure resistance, allowing them to withstand extreme water pressure conditions.
- Long service life, as PPR Type 3 pipes are resistant to corrosion and scaling.





